1. 关联容器
1. 关联容器
关联容器指set和map,这两种容器都是有序的,依靠内部的红黑树维护。
001 两数之和
给定一个整数数组 nums 和一个目标值 target,请你在该数组中找出和为目标值的那 两个 整数,并返回他们的数组下标。
给定 nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9
因为 nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9
所以返回 [0, 1]
解答:
注意:
- 不能排序,因为要返回下标序列,排序会打乱
- 这里需要用map记录而不是set,因为需要记录下标
对比一下167题输入的是有序数组,015三数之和要求返回的是数字组合而不是下标。
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
map<int,int> m;
vector<int> res{-1,-1};
if(nums.size()==0) return res;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)
{
int another = target - nums[i];
if(m.find(another)!=m.end())
{
res[0]=m[another];
res[1]=i;
}
else
m[nums[i]]=i;
}
return res;
}
012 整数转罗马数字
罗马数字包含以下七种字符: I, V, X, L,C,D 和 M。给定一个整数,将其转为罗马数字。输入确保在 1 到 3999 的范围内。
输入: 1994
输出: "MCMXCIV"
解释: M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90, IV = 4.
解答:
遍历从M到I的所有罗马数字,遇到合适的就填进res中,同时num减少。
string intToRoman(int num) {
vector<pair<int, string>> vec;
vec.push_back(make_pair(1000, "M"));
vec.push_back(make_pair(900, "CM"));
vec.push_back(make_pair(500, "D"));
vec.push_back(make_pair(400, "CD"));
vec.push_back(make_pair(100, "C"));
vec.push_back(make_pair(90, "XC"));
vec.push_back(make_pair(50, "L"));
vec.push_back(make_pair(40, "XL"));
vec.push_back(make_pair(10, "X"));
vec.push_back(make_pair(9, "IX"));
vec.push_back(make_pair(5, "V"));
vec.push_back(make_pair(4, "IV"));
vec.push_back(make_pair(1, "I"));
//vec的顺序是从大到小
string res="";
for(int i=0;i<vec.size();i++)
{
//先尝试最大的
while(num>=vec[i].first)
{
num-=vec[i].first;
res+=vec[i].second;
}
}
return res;
}
013 罗马数字转整数
罗马数字包含以下七种字符: I, V, X, L,C,D 和 M。
字符 数值
I 1
V 5
X 10
L 50
C 100
D 500
M 1000
输入: "LVIII"
输出: 58
解释: L = 50, V= 5, III = 3.
解答:
转化规则:前一个数小于后一个数,则前一个数为负记入总数,反之为正记入总数。
int romanToInt(string s) {
map<char,int> mymap;
mymap.insert(make_pair('M',1000));
mymap.insert(make_pair('D', 500));
mymap.insert(make_pair('C', 100));
mymap.insert(make_pair('L', 50));
mymap.insert(make_pair('X', 10));
mymap.insert(make_pair('V', 5));
mymap.insert(make_pair('I', 1));
int res=0;
if(s.size()==0) return 0;
for(int i=0;i<s.size()-1;i++)
{
if(mymap[s[i]]<mymap[s[i+1]])
res-=mymap[s[i]];
else
res+=mymap[s[i]];
}
res+=mymap[s.back()];
return res;
}
017 电话号码的字母组合
给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意 1 不对应任何字母。
输入:"23"
输出:["ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf", "cd", "ce", "cf"].
解答:
需要关注临时容器,依靠push的作用增添新元素。
vector<string> letterCombinations(string digits) {
map<char, string> mp;
mp['2'] = { "abc" };
mp['3'] = { "def" };
mp['4'] = { "ghi" };
mp['5'] = { "jkl" };
mp['6'] = { "mno" };
mp['7'] = { "pqrs" };
mp['8'] = { "tuv" };
mp['9'] = { "wxyz" };
vector<string> res;
if (digits.size() == 0) return res;
else res.push_back(""); //一定要做这一步不然循环都进不去
for(auto digit:digits)
{
string letter = mp[digit];
//需要做一个临时容器,否则会污染
vector<string> tmp;
for(auto oldstring:res)
for(auto newletter:letter)
tmp.push_back(oldstring+newletter);
res=tmp;
}
return res;
}
049 字母异位词分组
给定一个字符串数组,将字母异位词组合在一起。字母异位词指字母相同,但排列不同的字符串。
输入: ["eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"],
输出:
[
["ate","eat","tea"],
["nat","tan"],
["bat"]
]
解答:
如何判定是否异位相似:对每个字符串排序,将结果插入map中,最后再取出来。
vector<vector<string>> groupAnagrams(vector<string>& strs) {
vector<vector<string>> res;
map<string,vector<string>> m;
if(strs.size()==0) return res;
for(auto str:strs)
{
string tmp = str;
sort(tmp.begin(),tmp.end());
m[tmp].push_back(str);
}
for(auto x:m)
res.push_back(x.second);
return res;
}
138 复制带随机指针的链表
给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
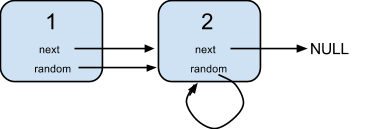
解答:
克隆每个节点需要干三件事:val, next, random,由于random的缘故我们需要一个map<Node*,Node*>来记录原来的节点和克隆节点的对应关系。
注意
- 必须
m[NULL]=NULL - 复制时,必须由
origin_index在前开路 - 添加随机时,两者同行
- 添加随机时需要重置
Node* copyRandomList(Node* head) {
//用map记录
if (!head)
return NULL;
Node* clone = new Node(head->val, NULL, NULL);
Node* clone_index = clone;
Node* origin_index = head;
map<Node*, Node*> mp;
mp[head] = clone;
mp[NULL] = NULL; //!非常重要
//先不复制随机
while(origin_index->next){
Node* newNode=new Node(origin_index->next->val,NULL,NULL);
clone_index->next=newNode;
mp[origin_index->next]=newNode;
clone_index=clone_index->next;
origin_index=origin_index->next;
}
//添加随机
clone_index = clone; //重置
origin_index = head;
while (clone_index)
{
clone_index->random = mp[origin_index->random];
clone_index = clone_index->next;
origin_index = origin_index->next;
}
return clone;
}
146 LRU缓存机制
设计和实现一个 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存机制。它应该支持以下操作: 获取数据 get 和 写入数据 put 。
获取数据 get(key) - 如果密钥 (key) 存在于缓存中,则获取密钥的值(总是正数),否则返回 -1。
写入数据 put(key, value) - 如果密钥不存在,则写入其数据值。当缓存容量达到上限时,它应该在写入新数据之前删除最近最少使用的数据值,从而为新的数据值留出空间。
解答:
数据结构的核心:List存数据,map记录某个数据在list中的位置,我们每次get和put都需要维护这两个数据结构。
无论是get还是put都需要先判断mp中是否已经存在!
记住:优先考虑如何更新map,然后再是删除list操作
class LRUCache {
private:
//list参数:key,val
list<pair<int, int>> l;
//map参数:key,iterator(这个key在list中的顺序)
map<int, list<pair<int, int>>::iterator> m;
int cap;
public:
LRUCache(int capacity) {
cap = capacity;
}
int get(int key) {
//it返回的不是顺序,而是map的pair
//it指向map中发现key的位置(一个pair,包含key和iterator)
//it->second指向list的iterator
//it->second->second指向val
auto it = m.find(key);
if (it == m.end())
return -1;
//不能放到erase之后!!!!
int val = it->second->second;
//更新list
l.push_front(make_pair(key, val));
//更新map必须在l之后!!!!!
m[key] = l.begin();
l.erase(it->second);
return it->second->second;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
auto it = m.find(key);
if (it != m.end())
//l的erase参数是iterator
l.erase(it->second);
l.push_front(make_pair(key, value));
m[key] = l.begin();
if (l.size() > cap)
{
int key = l.back().first;
//m的erase参数是key
//擦去的时候map擦key,list擦iterator
m.erase(key);
l.pop_back();
}
}
};
205 同构字符串
给定两个字符串 s和 t,判断它们是否是同构的。如果s中的字符可以被替换得到 t ,那么这两个字符串是同构的。
输入: s = "paper", t = "title"
输出: true
输入: s = "foo", t = "bar"
输出: false
解答:
抽象为ABAC类型
bool isIsomorphic(string s, string t) {
return abstract(s)==abstract(t);
}
string abstract(string str)
{
string tmp=str;
int flag=0;
map<char,char> m;
for(int i=0;i<str.size();i++)
{
if(m.find(str[i])==m.end())
{
tmp[i]='a'+flag;
m[str[i]]=tmp[i];
flag++;
}
else
tmp[i]=m[str[i]];
}
return tmp;
}
208 实现Trie(前缀树)
实现一个 Trie (前缀树),包含 insert, search, 和 startsWith 这三个操作。
Trie trie = new Trie();
trie.insert("apple");
trie.search("apple"); // 返回 true
trie.search("app"); // 返回 false
trie.startsWith("app"); // 返回 true
解答:
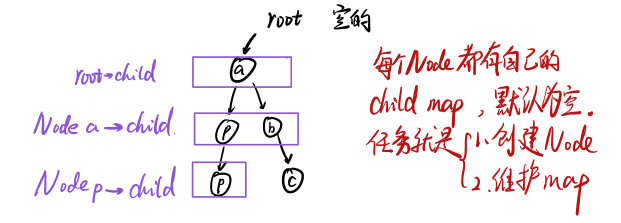
注意打上leaf不表示这一脉真的结束了,而是表示从头到这个节点,在字典里有对应,方便search操作。
class Trie {
public:
struct TrieNode
{
map<char,TrieNode*> child;
bool isLeaf;
TrieNode():isLeaf(false){};
};
TrieNode* root;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
Trie() {
root=new TrieNode();
}
/** Inserts a word into the trie. */
void insert(string word) {
TrieNode* cur = root;
for(auto c:word)
{
auto it=cur->child.find(c);
if(it==cur->child.end())
cur->child.insert(make_pair(c,new TrieNode()));
cur=cur->child[c];
}
cur->isLeaf=true;
}
/** Returns if the word is in the trie. */
bool search(string word) {
TrieNode* cur = root;
for(auto c:word)
{
auto it=cur->child.find(c);
if(it==cur->child.end())
return false;
cur=cur->child[c];
}
return cur->isLeaf;
}
/** Returns if there is any word in the trie that starts with the given prefix. */
bool startsWith(string prefix) {
TrieNode* cur = root;
for(auto c:prefix)
{
auto it=cur->child.find(c);
if(it==cur->child.end())
return false;
cur=cur->child[c];
}
return true;
}
};
217 存在重复元素
给定一个整数数组,判断是否存在重复元素。如果任何值在数组中出现至少两次,函数返回 true。如果数组中每个元素都不相同,则返回 false。
输入: [1,2,3,1]
输出: true
解答:
SET去重
bool containsDuplicate(vector<int>& nums) {
set<int> s;
for(auto num:nums)
s.insert(num);
return s.size()!=nums.size();
}
219 存在重复元素 II
给定一个整数数组和一个整数 k,判断数组中是否存在两个不同的索引 i 和 j,使得 nums [i] = nums [j],并且i和j的差的绝对值最大为k。
输入: nums = [1,2,3,1], k = 3
输出: true
解答:
bool containsNearbyDuplicate(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
if(nums.size()==0||k==0) return false;
map<int,int> m;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)
{
auto it = m.find(nums[i]);
if(it==m.end())
m[nums[i]]=i;
else
{
if(i-m[nums[i]]<=k)
return true;
else
m[nums[i]]=i;
}
}
return false;
}
220 存在重复元素 III
给定一个整数数组,判断数组中是否有两个不同的索引 i 和 j,使得 nums [i]和nums [j]的差的绝对值最大为 t,并且 i 和 j 之间的差的绝对值最大为 k。
输入: nums = [1,2,3,1], k = 3, t = 0
输出: true
解答:
这道题也可以按219的模板来做,但速度就很感人了。可以维护一个窗口,大小不超过k,滑动窗口比较nums的值是否满足要求。采用set来存储窗口的值。
bool containsNearbyAlmostDuplicate(vector<int>& nums, int k, int t) {
set<long long> s;
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < nums.size(); i++)
{
if (i - j > k)
{
s.erase(nums[j]);
j++;
}
auto it = s.lower_bound((long long)nums[i] - t);//有可能nums[i] - t是个负数
if (it != s.end() && abs(nums[i] - *it) <= t)//必须要double check
return true;
s.insert(nums[i]);
}
return false;
}
3. 容器适配器
指stack,queue的运用
020 有效的括号
给定一个只包括 '(',')','{','}','[',']' 的字符串,判断字符串是否有效。
输入: "{[]}"
输出: true
输入: "([)]"
输出: false
解答:
switch一定要跟break,不然会顺序执行。
switch(1) {
case 1 : cout << '1'; // 打印 "1",
case 2 : cout << '2'; // 然后打印 "2"
}
最后要判断栈是否为空,防止输入[,返回true这种情况
bool isValid(string s) {
if(s.size()==0) return true;
stack<char> stk;
for(auto c:s)
{
switch(c)
{
case '(': stk.push('('); break;
case '[':stk.push('['); break;
case '{':stk.push('{'); break;
case ')':
if(stk.empty()||stk.top()!='(') return false;
else stk.pop();
break;
case ']':
if(stk.empty()||stk.top()!='[') return false;
else stk.pop();
break;
case '}':
if(stk.empty()||stk.top()!='{') return false;
else stk.pop();
break;
}
}
return stk.empty();
}
21 括号生成
给出 n 代表生成括号的对数,请你写出一个函数,使其能够生成所有可能的并且有效的括号组合。
例如,给出 n = 3,生成结果为:
[
"((()))",
"(()())",
"(())()",
"()(())",
"()()()"
]
解答:
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> res;
vector<string> generateParenthesis(int n) {
gen("", 0, 0, n);
return res;
}
void gen(string str,int numLeft,int numRight,int n){
//剪枝条件
if(numRight>numLeft) return; //右括号数目大于左括号,凉凉
if(numRight>n||numLeft>n) return; //某一种括号太多,凉凉
//收集条件
if(numLeft== n && numRight == n) {res.push_back(str); return;}
gen(str+'(',numLeft+1,numRight,n);
gen(str+')',numLeft,numRight+1,n);
return;
}
};
150 逆波兰表达式求值
根据逆波兰表示法,求表达式的值。有效的运算符包括 +, -, *, / 。每个运算对象可以是整数,也可以是另一个逆波兰表达式。
输入: ["4", "13", "5", "/", "+"]
输出: 6
解释: (4 + (13 / 5)) = 6
输入: ["2", "1", "+", "3", "*"]
输出: 9
解释: ((2 + 1) * 3) = 9
解答:
从前往后遍历数组,遇到数字则压入栈中,遇到符号,则把栈顶的两个数字拿出来运算,把结果再压入栈中,直到遍历完整个数组,栈顶数字即为最终答案。
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens) {
stack<int> s;
for (int i = 0; i < tokens.size(); i++)
{
string c = tokens[i];
if (c == "+" || c == "-" || c == "*" || c == "/")
{
//栈存取顺序!
int val2 = s.top();
s.pop();
int val1 = s.top();
s.pop();
if (c == "+")
{
val1 += val2;
s.push(val1);
}
if (c == "-")
{
val1 -= val2;
s.push(val1);
}
if (c == "*")
{
val1 *= val2;
s.push(val1);
}
if (c == "/")
{
val1 = val1 / val2;
s.push(val1);
}
}
else
s.push(stoi(tokens[i]));
}
return s.top();
}
155 最小栈
设计一个支持 push,pop,top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
解答:
维护两个栈:一个存最小,一个存数据。注意一定要小于等于,为了pop的一致性。
class MinStack {
public:
stack<int> data;
stack<int> min;
/** initialize your data structure here. */
MinStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
data.push(x);
if(min.empty()||x<=getMin())
min.push(x);
}
void pop() {
if(data.top()==min.top())
min.pop();
data.pop();
}
int top() {
return data.top();
}
int getMin() {
return min.top();
}
};
225 用队列实现栈
解答:
可以用双端队列,但比较慢,而且没什么意思。
class jr225_MyStack {
//双队列交替存储
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
MyStack() {
}
queue<int> q1;
queue<int> q2;
/** Push element x onto stack. */
void push(int x) {
if (q1.empty() && q2.empty())
q1.push(x);
else if (q2.empty())
{
q2.push(x);
while (!q1.empty())
{
q2.push(q1.front());
q1.pop();
}
}
else//q1.empty
{
q1.push(x);
while (!q2.empty())
{
q1.push(q2.front());
q2.pop();
}
}
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
int pop() {
int val;
if (!q1.empty())
{
val= q1.front();
q1.pop();
}
else if (!q2.empty())
{
val = q2.front();
q2.pop();
}
return val;
}
/** Get the top element. */
int top() {
if (!q1.empty())
return q1.front();
else if (!q2.empty())
return q2.front();
else
return 0;
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
bool empty() {
return q2.empty() && q1.empty();
}
};
232 用栈实现队列
解答:
class MyQueue {
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
stack<int> s1, s2;
MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
void push(int x) {
while (!s2.empty()) {
s1.push(s2.top());
s2.pop();
}
s2.push(x);
while (!s1.empty()) {
s2.push(s1.top());
s1.pop();
}
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
int pop() {
int a = s2.top();
s2.pop();
return a;
}
/** Get the front element. */
int peek() {
return s2.top();
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
bool empty() {
return s2.empty();
}
};